By Leo Thomas
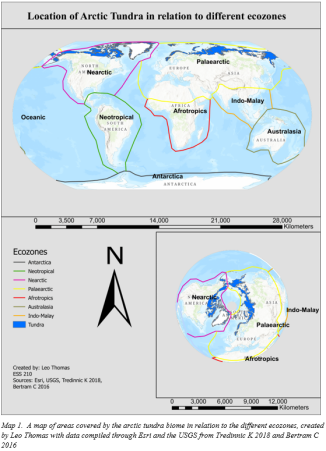
The biome of focus for this paper is the arctic tundra which encompasses roughly 9,654,211 square kilometers of land at high northern latitudes with the lowest points around 55 degrees north and the highest points occurring past 80 degrees north (see map 1) (Christopherson & Birkeland 2019). The biogeographic realms or Ecozones this biome occurs in are the “Nearctic” and “Palearctic” (refer to map 1), with the majority occurring in the “Nearctic”. This biome can be identified as a treeless region containing permafrost featuring cold, harsh winters for most of the year (UCMP Berkeley 2019). The most major threats to this biome are a warming climate, pollution, and invasive species (Koyama et. al 2013). The focus of this narrative is to educate the reader on the importance of this biome and pertinent issues threatening it.
Features of the Area
The arctic tundra is a harsh biome characterized by unique physical features, abrasive climatic features, and ecological features that have adapted to function in such a challenging environment.
Physical Features
Physical features in the arctic tundra as seen in table 1 include permafrost or gelisols (ground within 2 meters of the soil surface that remains at below 0 degrees for over 2 years), and high latitudes (UCMP Berkeley 2019).
Climatic Features
Climatic features for this biome include cold temperatures year-round (with the mean annual temperature being -7 degrees Celsius as stated by Koyama et. al 2019), and a low annual precipitation according to Koyama et. al 2019 of 400mm (half of which falls as snow); these climatic features lead to a short growing season in warmer months when the active layer above the permafrost slightly thaws (Christopherson & Birkeland 2019).
Ecological Features
Because of the unforgivingly cold yet dry climate, the most defining ecological feature of the arctic tundra is a treeless landscape (UCMP Berkley 2019). Low biodiversity is another major ecological feature of the arctic tundra with producers mainly consisting of deciduous shrubs, mosses, graminoids (small herbaceous grass like plants), and lichens (koyama et. al 2013) while primary consumers mainly consist of caribou, lemmings, voles, arctic hares, and squirrels (UCMP Berkeley 2019) and secondary/tertiary consumers mainly consist of arctic foxes, polar bears, wolves, and some migratory birds (UCMP Berkeley 2019). Many of the non-migratory species that inhabit this biome are also endemic species (species that only inhabit one geographic location) (UMCP Berkeley 2019). Due to the low biodiversity in the biome, another ecological feature is low net primary productivity and biomass as found by Virtanen et. al 2012.

Issues of Concern
The most exigent issues facing the arctic tundra biome are thawing permafrost, invasive species, and mercury pollution. Permafrost is one of the main defining characteristics of the arctic tundra. However, because of warming temperatures, permafrost is thawing at an abnormally high rate. Without permafrost the arctic tundra would be nonexistent as permafrost keeps water near the top layers of soil, which allows specially adapted plants to survive (NSIDC 2020). Pollution is another major concern for this biome as human related activities have led to a large amount of gaseous mercury pollution which is being taken up by soil, snowpack, and water in the arctic tundra (see figure 1) at a higher rate than any other biome (Obrist et. al 2017). The high uptake of gaseous mercury by this biome has led researchers Obrist et. al to believe that the arctic tundra is an extremely important mercury sink in the global mercury cycle, this uptake in mercury threatens animal populations through bioaccumulation (the increased accumulation of toxins up the trophic pyramid) and according to Obrist et al 2017 “Arctic rivers annually transport large amounts of Hg (mercury) into the arctic ocean”. Invasive species also threaten the wellbeing of the arctic tundra as trees and vascular plants which used to only exist in the Ecotones (areas akin to biome purgatory that bridge the gap between two biomes sharing features from each) are beginning to crop up in areas of thawing permafrost (Katariina et. al 2017). An impact of these plants migrating into the tundra is a negative impact on (an already low) biodiversity and net annual productivity (refer to figure 2) as these larger vascular plants win competitions for sunlight and nutrients against the smaller native plants (Virtanen et. al 2012). Overall though this biome is a very important sink for things like mercury it is being threatened and destroyed by permafrost thaw, pollution, and invasive species.


Potential Climate Change Impacts and Biogeographical Change
Climate change is the main reason for issues in the arctic tundra leading to permafrost thaw and invasive species being able to survive in areas previously occupied by only species which were heavily adapted for living in such an unforgiving environment. This change has been observed by Katariina et. al 2017 as they stated that temperatures in this biome have raised 2-3 degrees Celsius since 1965. The thawing of permafrost does not only affect the tundra, but the carbon cycle of the entire world. Permafrost slows decay of organic matter (decay produces CO2), and as the permafrost thaws, the biotic activity in the soil increases causing more decay, more decay produces more CO2, and more CO2 causes more climate change. This positive climate feedback is called Permafrost carbon feedback and causes these areas which were originally carbon sinks (carbon storage areas) to turn into carbon sources (areas which release carbon). Biogeographical change (the change in species distribution and richness) goes hand in hand with a warming environment because as permafrost melts it becomes harder for endemic species to survive while invasive species have an easier time surviving in the biome, which as previously stated reduces biodiversity (Virtanen et. al 2012). In conclusion the positive climate feedback caused by rising temperatures causes temperatures to rise more and encourages more biogeographical change in the area.
Conclusions
Overall, the arctic tundra is a unique biome characterized by permafrost and a treeless landscape that provides essential services to the earth such as mercury uptake and carbon storage. Though this biome provides important earth services it is in danger due to permafrost thaw from warming temperatures, mercury pollution, and invasive species. If this biome were to collapse entirely it would no longer be able to provide its vital aid in the mercury and carbon cycles and would instead begin leaching more unwanted pollutants into the environment.